Single Fiber Solutions for CWDM and DWDM Networks
It is well known that there are two transmission ways for fiber optical network, single fiber transmission and dual fiber transmission. From the name, it is easy to learn that the fiber amount is the main difference of these two transmission ways. For the dual fiber transmission, there should be totally two optical fibers, one for transmitting signals, and the other for receiving signals. But for the single fiber transmission, it only requires one optical fiber that can transmit and receive signals at the same time. This feature makes the network deployment easier and the network deployment cost lower than that of dual fiber one, especially in WDM network deployment. In this paper, it will mainly introduce the single fiber solution and its applications in CWDM and DWDM networks.
Single Fiber Solution
Single fiber solution can be also called bidirectional (BiDi) solution designed for carrying signals in both sides of one optical fiber simultaneously. When the single fiber network runs, the signals transmitted from the two sides feature different wavelengths to ensure the dual way transmission. Compared to the dual fiber network, the easy-to-deploy single fiber network would be a good choice for those who have limited budgets but need for bigger network capacity. As for its application, it is very popularly used in Point to Point, Ring or linear Add and Drop, where installing new fibers is impracticable or uneconomical. It can be also used for promoting the reliability of an existing dual fiber network, in which there are one optical fiber for work and the other one for protection.
Single Fiber CWDM Network
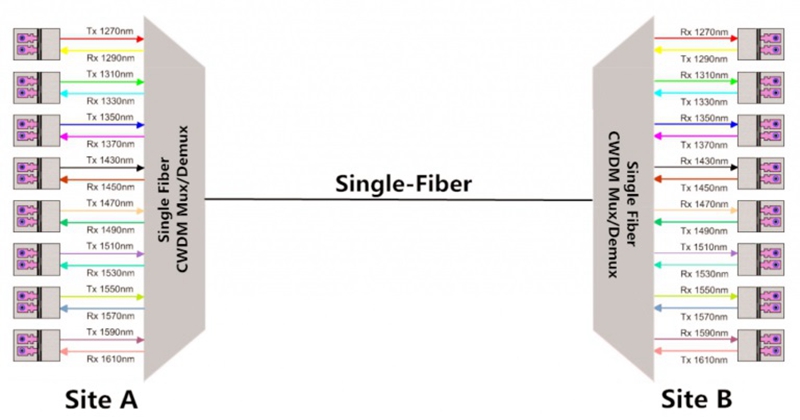
The single fiber CWDM network enables the signals with different wavelengths to be transmitted through a signal fiber, which results in a network capacity boost in metro and access networks. As each signal beam can be carried via different channel independently, the different data rates and protocols (T1, T3, Ethernet, Serial, etc) can be transmitted for the different users or applications. To better know how does the single fiber CWDM network work, here offers a figure that shows a 8 channel single fiber CWDM network design.
From the figure, we can learn there are two 8 channel CWDM Mux Demux connected by a single fiber for transmitting 16 signals with different wavelengths and the 16 wavelengths are divided into 8 pairs for bidirectional transmission. On the site A, 8 wavelengths are used for transmitting signals and others for receiving signals. While on the site B, the wavelengths for the TX and RX on the CWDM Mux Demux are all reversed to ensure the performance of the single fiber CWDM network. For instance, the 1270 nm on the site A is the first transmitting wavelength but the first receiving wavelength on the site B. As a result, the signal with 1270 nm can be totally transmitted from site A to site B via the single fiber.
Single Fiber DWDM Network
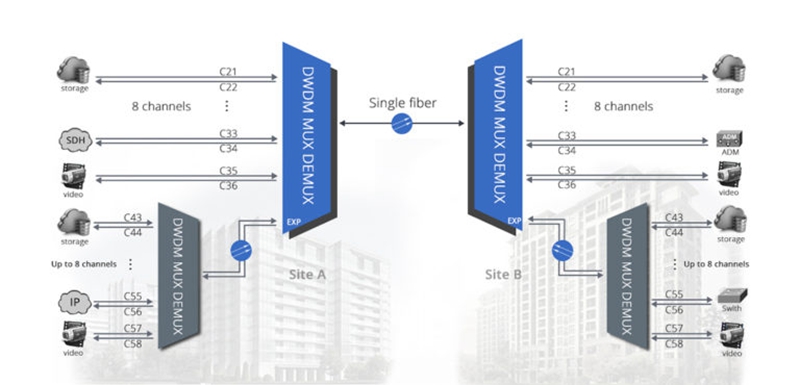
The single fiber DWDM network also takes full use of the wavelength division multiplexing technology that can greatly expand the capacity over the existing optical network, especially for the long transmission network. Compared to the CWDM one, it can be designed with more channels for larger data signals and can support the network with a much longer distance. What’s more, if the transmission distance is too long, the optical amplifier can be used to enhance the signals. On the other hand, all these advantage makes the cost to deploy a single fiber DWDM network much higher than the CWDM one. Besides, here offers the figure of a single fiber DWDM network design for your reference.
The figure shows a complicated a single fiber DWDM network design that uses two 8 channel DWDM Mux Demux in the main link for single fiber transmission. As for the wavelength feature of the TX and RX for the ports on the DWDM Mux Demux, it is similar to the CWDM one, but the channel spacing is denser. What’s more, except for the existing channels in the main single fiber DWDM link, there can be more channels added into the expansion port of the link for carrying larger data signals. In short, although the cost for deploying single fiber DWDM network is so expensive, it is still a good solution that can make full use of the fiber link to transmit more signals at a much longer distance.
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, the single fiber WDM solution is an ideal choice for those who have limited budgets but need for bigger network capacity. As there are two single fiber WDM solutions available, which one to choose just depends on the network need and budget. The single fiber CWDM network would be more economical but can not transmit as much signals as the DWDM one can, while the DWDM is highly recommended for large and long transmission that would cost more.